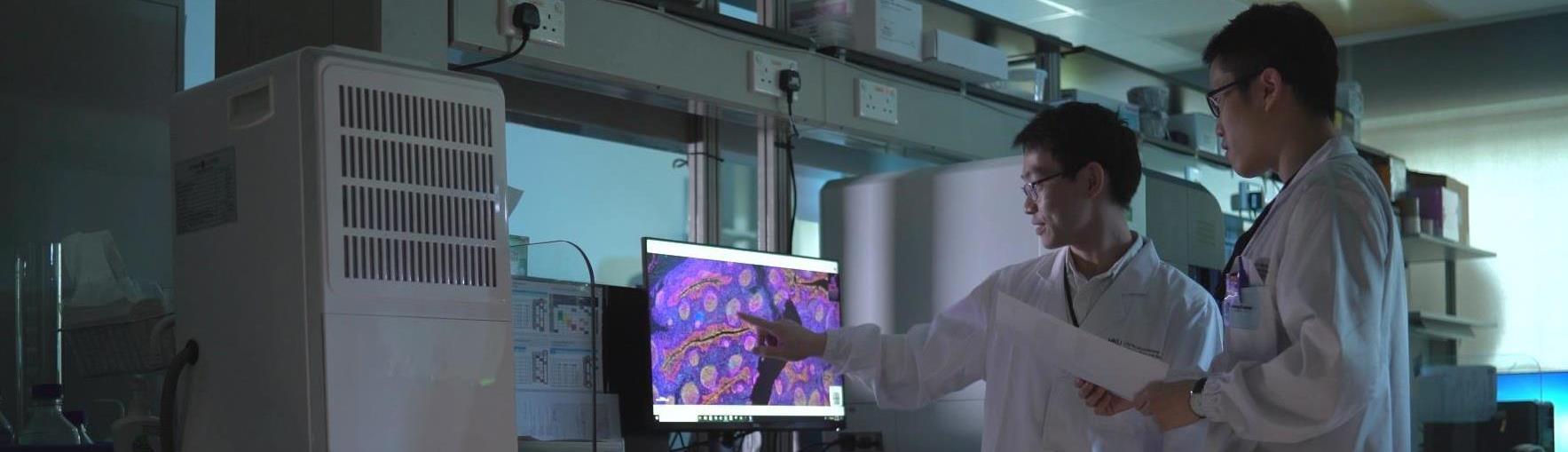
1. What is Colonoscopy? 什麼是大腸鏡檢查?
大腸鏡檢查可以檢測到大腸的異常狀況,包括大腸癌及瘜肉。 在檢查時, 醫生會用一支柔軟的大腸內視鏡為病人檢查大腸的各部份。如果發現有大腸瘜肉,醫生會在評核情況後將瘜肉切除以防止瘜肉變成為大腸癌。目前,大腸鏡檢查是診斷和預防大腸癌的最佳辦法。
2. What device is used during the colonoscopy examination? 醫生在檢查時會使用什麼儀器?
A colonoscope, a long, thin and flexible instrument, is used to examine the colon. It has a tiny camera with light source at the tip allowing the doctor to see the inside of the colon on a television screen. The doctor can take tissue sample, remove polyps and perform other diagnostic or therapeutic procedures with a colonoscope if necessary.
醫生會使用大腸鏡進行檢查。大腸鏡是一條柔軟的內視鏡,用於檢測大腸狀況。在檢查時,醫生可以按病情需要抽取組織樣本、切除瘜肉及進行其他診斷或治療的程序。
3. What is colorectal cancer? 什麼是大腸癌?
Colorectum, also known as the large intestine, is the last part of our digestive system. Nutrients and fluids are absorbed as they pass through the digestive system. The remaining waste (faeces) pass out of the body through the large intestine and the anus.
結直腸,又稱為大腸,是消化系統的最後部分。食物飲品中的營養及水分會在消化道中被吸收,餘下未能吸收的會成為大便經由大腸及肛門排出。
Our body consists of a large number of cells with different functions. In normal circumstances, cells grow and divide in a controlled manner to keep our body healthy. When there is a change in genetic materials (mutation) in the colon cells, these cells can grow out of control. These abnormal cells may accumulate and form a polyp. Some of the polyps may progress to become cancer over a period of a few years to more than 10 years. Colorectal cancer can invade normal organs nearby and spread to other parts of the body.
人類的身體由大量細胞組成,並擁有不同的功能。在正常情況下,細胞會在受控制環境中生長及分裂以維持身體健康。若大腸細胞基因突變,將出現不正常生長,並逐漸積聚成瘜肉。經過幾年甚至乎多於十年的時間,瘜肉有可能病變成大腸癌。如果沒有適當治療, 大腸癌可以擴散到身體其他器官。
Colorectal cancer is the most common cancer and the second most common cause of cancer deaths in Hong Kong. It accounted for 17.3% of all new cancer cases in 2016 and 14.9% of all cancer deaths in 2017.
大腸癌是香港最常見的癌症及第二號癌症殺手。在2016年,17.3%新癌症案例為大腸癌;在2017年,在死於癌症患者中, 14.9%病人死於大腸癌。
Colorectal cancer patients can develop symptoms including rectal bleeding or change in bowel habit (refer to Q4). However, some patients with colon polyps or early stage colorectal cancer may not have symptoms. Therefore, screening of colorectal cancer is advisable to detect and prevent the disease in asymptomatic average-risk persons older than 45 years old and other persons at risk (refer to Q7).
大腸癌病患者可能有大便出血或大便習慣改變的症狀 (請參考第4題) 。但如果是早期大腸癌或只有大腸瘜肉,病人未必有任何症狀。我們建議45歲以上的市民及其他患大腸癌高風險人士 (請參考第7題),應進行大腸癌篩查。
4. What are the symptoms of colorectal cancer? 大腸癌有什麼症狀?
Symptoms include:
症狀包括:
- Passage of blood or a large amount of mucus in stool
大便帶血或大量黏液 - Change in bowel habit (diarrhoea or constipation) with unknown reasons and lasting for more than two weeks
無故情況下大便習慣改變,如腹瀉或便秘,並持續兩星期或以上 - Persistent urge after passing stool
大便後持續有便意 - Abdominal discomfort, including persistent pain, bloating, fullness or cramps
腹部不適,如持續疼痛、腹脹、飽脹或絞痛等 - Weight loss and tiredness with unknown reason
無故情況下體重下降及感到疲累
Although having these symptoms do not necessarily mean that you have colorectal cancer, you are advised to consult a doctor if you have these symptoms.
儘管你有以上的症狀, 也不代表你一定患上大腸癌。我們建議你應盡快求醫。
5. What is a colon polyp? 什麼是大腸瘜肉?
It is a growth of tissue on the inner lining of the colon. It is very common and affects around 1 in 4 people at some point in their lives. It can appear as a small protrusion or a bump on the colon wall. Polyps do not usually cause symptoms and are often detected on screening for colorectal cancer. Larger polyp may cause passage of blood or mucus in stool. Most of the polyps are non-cancerous but some of them can progress to cancer over time. There are several different types of polyps:
大腸瘜肉的形成是由於大腸內壁一些細胞基因突變, 以致不斷增生而形成的。大概每四個人中,就有一個人會患有大腸瘜肉。患者通常沒有症狀,並只會在大腸癌篩查時才發現瘜肉。患有大型瘜肉的病人有可能有大便帶血或黏液的情況。大部分瘜肉在早期都是良性的,但是經過長時間生長,瘜肉有機會變成腸癌。以下有幾種較常見的瘜肉:
- Adenoma – most cancers develop from adenoma polyp. Under the microscope, doctor can examine the growth pattern and the degree of dysplasia of an adenoma. There are two major growth patterns: tubular and villous. “Dysplasia” describes how much the polyp looks like cancer. Larger adenoma with villous growth pattern and “high-grade dysplasia” has a higher chance of progression to cancer. A group of adenoma is called “serrated” adenoma, which has a saw-tooth appearance under the microscope. There are 2 types of serrated adenoma: sessile serrated adenoma and traditional serrated adenoma. Because of the risk of progression to cancer, adenoma should be removed from the colon.
腺瘤型 – 大部分癌症由此類瘜肉形成。醫生可以透過顯微鏡檢驗腺瘤的生長模式及病變程度。此類瘜肉生長模式大致分為兩種:管狀或絨毛狀。其中, 大型絨毛狀且高病變程度的腺瘤比較大機會發展成惡性。另一群腺瘤為鋸齒形腺瘤,又分為無蒂鋸齒形及傳統鋸齒形。在大腸鏡檢查時, 醫生會切除這些腺瘤型瘜肉,以防止病變成癌症。
Hyperplastic polyps – They are usually small and are often found in the sigmoid and the rectum. Generally, they have little or almost no potential to become cancerous.
增生型 – 比較微細,多發現於乙型結腸或直腸,基本上不會病變成癌症Inflammatory polyps – They are most often found in patients with ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, and is caused by chronic inflammation of the colon wall.
炎症型 – 多發現於潰瘍性結腸炎或克隆氏症患者,慢性大腸壁發炎產生此類瘜肉
6. Who is at a higher risk of colorectal cancer? 什麼是患大腸癌的風險因素?
有些風險因素可使你比一般人較高機會患上大腸癌,一部分的因素是和飲食及生活習慣有關,另一部分則可能是基因遺傳的因素。
Lifestyle factors include:
生活習慣因素包括:
- Being overweight or obese
過重或肥胖 - Physical inactivity
少運動 - Diet low in fiber and high in red meat
低纖及高動物脂肪的飲食習慣 - Smoking 吸煙
- Heavy alcohol use 大量飲酒 Other factors that are not modifiable: 其他不能改變的因素:
- Old age – Colorectal cancer is much more common after age of 50
年齡增長 – 大腸癌患者普遍大於50歲 - Personal history of colorectal cancer or polyps
病人有大腸癌或瘜肉的病史 - Family history of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps
家庭病歷涉及大腸癌及腺瘤型瘜肉 - Personal history of inflammatory bowel disease
病人患有炎症性腸炎 - Having an inherited syndrome that is linked with colorectal cancer such as Lynch syndrome (hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer, HNPCC), familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and other rarer syndromes
病人有大腸癌有關的遺傳綜合症如連氏綜合症、家族性結直腸瘜肉綜合症或其他罕見綜合症
7. When should I start screening for colorectal cancer? 我應該在什麼時候開始作大腸癌篩查?
市民應在45歲開始作大腸癌篩查。大腸鏡檢查是現時最有效篩查和預防大腸癌的方法。如果檢查時發現瘜肉, 醫生會切除這些瘜肉以預防大腸癌。 Persons with first-degree relative diagnosed with colorectal cancer should start screening 10 years younger than the age at which their youngest first-degree relative was diagnosed or at age 40.
如果有直系親屬曾患大腸癌,你應在該位親屬確診的年齡早10年時或大約在40歲左右開始接受大腸鏡檢查。 Persons with relatives diagnosed with hereditary colon cancer syndrome such as Lynch syndrome and familial adenomatosis polyposis are at increased risk of having colon polyps and colorectal cancer. Patients with long standing inflammatory bowel disease also have increased risk of colorectal cancer. They should consult their doctor on the optimal timing for screening of colorectal cancer.
如果你有家族成員患有遺傳性的大腸癌基因綜合症如連氏綜合症或家族性結直腸瘜肉綜合症,或本身患有炎症性腸炎多年,你會有較高機會患上大腸癌。你應徵詢醫生意見應在甚麼時候作大腸癌檢查。
If you have symptoms of colon disease such as passing blood in stool or change in bowel habit, you are also advised to consult a doctor for further evaluation.
若果你有大腸癌症狀如大便帶血或大便習慣改變,應盡快求醫。
8. What will the doctor do if a polyp is found during colonoscopy? 如果在大腸鏡檢查中發現瘜肉,醫生會如何處理?
Doctors will generally recommend removal of colon polyps because some of these polyps can develop into cancer with time. Most of the pre-cancerous polyps can be removed during routine colonoscopy. Doctors can remove a polyp by using a wire loop (snare) or a biopsy forcep. If the polyp is too large, it may need to be treated by specialized method during colonoscopy or by removing part of the bowel surgically.
如果在大腸鏡檢查時發現瘜肉, 一般來說, 醫生會切除這些瘜肉以預防大腸癌。大部分瘜肉都可以在大腸鏡檢查時切除。但如果瘜肉太大,則未必可以在常規大腸鏡檢查時切除。醫生有可能要用一些專門的內視鏡治療方法切除瘜肉或以手術方法切除部分大腸以清除瘜肉。
9. What happens if colorectal cancer is detected? 如在大腸鏡檢查中診斷到大腸癌,應如何處理?
If a tumour mass is detected during colonoscopy, tissue sample will be taken for evaluation. After the diagnosis of colorectal cancer is confirmed, you will be referred to doctors specializing in treatment of the disease. Imaging will be arranged to evaluate the extent of disease involvement. Depending on the location of tumour and extent of disease involvement, treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy and/ or radiotherapy. There is a higher chance of cure if cancer is found at an early stage.
醫生如在大腸鏡檢查中發現病人有腫瘤,會抽取組織樣本並送往化驗。病人若確診為大腸癌,會被轉介至專科醫生。醫生會安排病人作掃描檢查。之後,醫生會根據腫瘤位置及癌細胞擴散程度而建議病人接受適合的治療, 包括手術、化療及/或電療。一般而言, 如果是早期大腸癌的話,患者康復的機會會較高。
10. What does it feel when I am having a colonoscopy? 我在進行大腸鏡檢查時,會有什麼感覺?
You will be given “conscious sedation” when you have colonoscopy. This will help you relax and to relieve pain, but you may stay awake during the procedure. During colonoscopy, as the scope is moved or air is passed into the colon, you may feel bloating or abdominal cramping. If any, the discomfort is usually mild and you won’t usually feel pain. The most common type of sedation also has a mild amnesiac effect, thus most patients are unable to remember the procedure afterwards.
在大腸鏡檢查前,病人會先接受 “鎮靜麻醉”。醫生會為病人注射藥物使病人放鬆及減少檢查時的不適, 但是病人在檢查時可能仍有知覺。在進行大腸鏡檢查中,醫生放入大腸鏡時會注入空氣, 病人可能會感到輕微不適但一般不會感到痛楚。有很多病人在麻醉後,對檢查過程只有模糊的記憶。